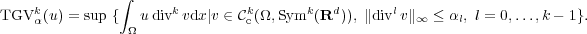
Most mathematical formulations of inverse problems and in particular of mathematical imaging problems are cast in the form of minimizing the sum of a fidelity term and a regularization term. Due to its ability to detect and preserve edges, the total variation of a function is widely used as a penalization functional in imaging.
However, total variation regularization is based on the assumption that the underlying image consists of piecewise constant regions. For natural images, this assumption is no longer valid causing the solutions to suffer from undesired staircasing artifacts.
Such limitations can be overcome by considering the total generalized variation for some order k ≥ 2 and positive weights α0,…,αk-1:
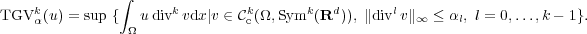
The test functions are symmetric k-tensor fields with pointwise restrictions on the divergences. Functions of bounded variation admit finite total generalized variation. In the simplest case of k = 2, dualizing yields the formal representation
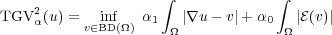
where v are vector fields of bounded deformation, i.e. their distributional symmetrized derivative 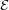 (v) is still a measure. This
can be interpreted as some optimal balancing between the first and second derivative. Consequently, it prefers piecewise
smooth images over staircase images in terms of penalization and is therefore well-suited for image processing
applications.
(v) is still a measure. This
can be interpreted as some optimal balancing between the first and second derivative. Consequently, it prefers piecewise
smooth images over staircase images in terms of penalization and is therefore well-suited for image processing
applications.
As TGVαk is a proper, convex and lower semi-continuous functional, it can be utilized as a penalty functional for variational imaging problems. Denoising and image reconstruction from undersampled Fourier data in MRI have been considered so far. Numerical results confirm the absense of staircasing artifacts and an improvement of visual image quality in comparison to TV.
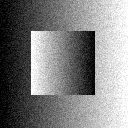 | 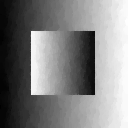 |  |
| noisy image | L2-TV denoising | L2-TGV α2 denoising |
| noisy |  | 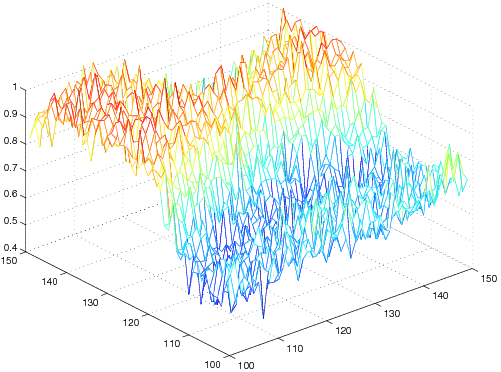 |
| L2-TV |  | 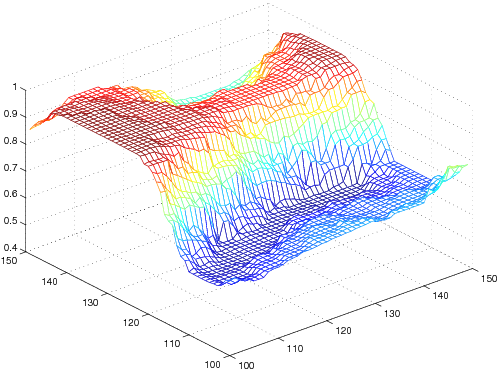 |
| L2-TGV α2 |  | 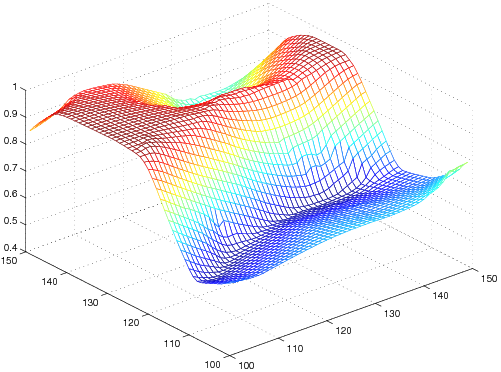 |
| L2-TGV α3 |  | 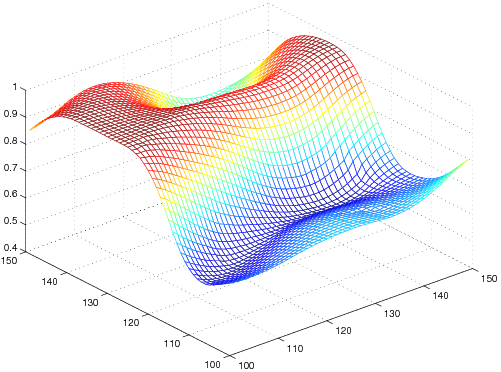 |
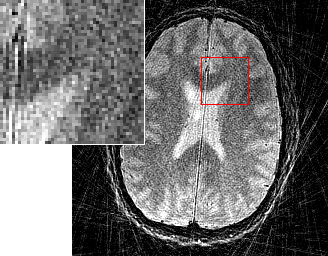 | 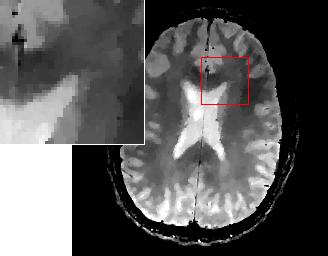 | 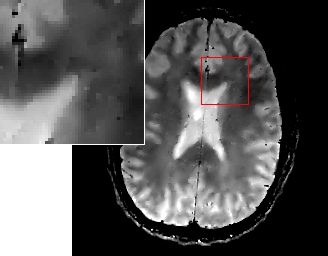 |
| MRI NUFFT | MRI TV | MRI -TGV α2 |