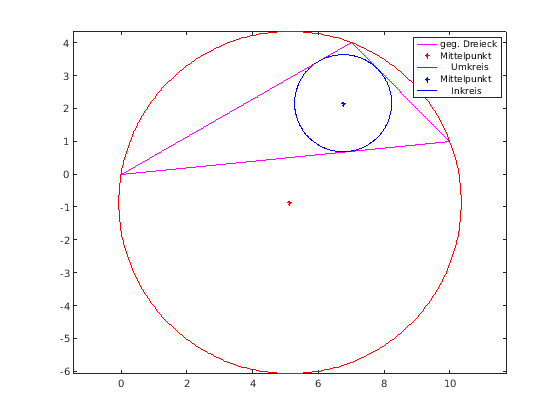
Umkreis und Inkreis eines Dreieck
Contents
Koordinaten des Dreiecks
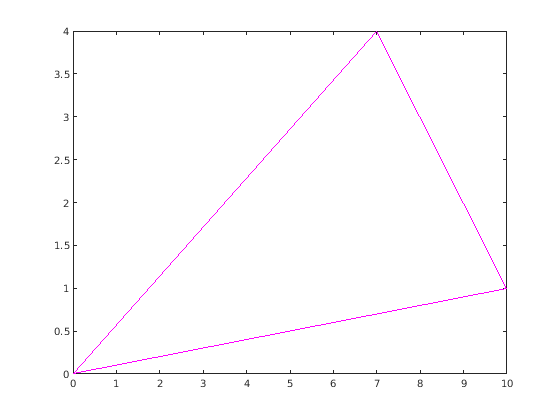
clear; clc; clf; A = [0 ; 0]; B = [10; 1]; C = [7;4]; % A = [0 ; 0]; % B = [3; 0]; % C = [2; 3]; % A = [0 ; -6]; % B = [7; 4]; % C = [-3;-3]; % Grafik plot([A(1) B(1) C(1) A(1)], [A(2) B(2) C(2) A(2)],'m-'); hold on
Umkreis
S1 = (A+B)/2; % Seitenmittelpunkt von Strecke BA S2 = (A+C)/2; n1 = cross( [A-B; 0], [0;0;1]); % Normalenvektor auf BA n1(3) = []; n1 = n1/norm(n1); n2 = cross( [C-A; 0], [0;0;1]); % Normalenvektor auf AC n2(3) = []; n2 = n2/norm(n2);
Gleichungssystem loesen
Mat = [ n1, -n2 ]; rhs = S2-S1; t = Mat\rhs;
Mittelpunkt aus Geradengleichung berechnen
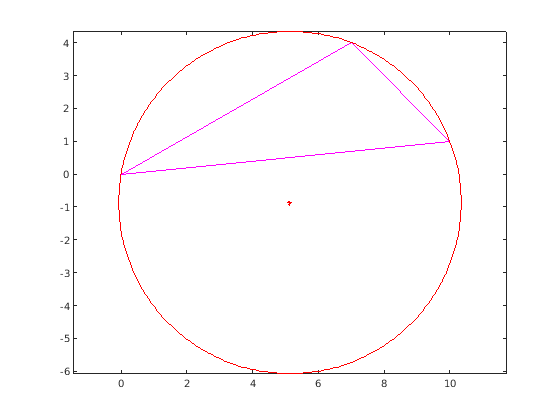
M = S1+n1*t(1)
N = S2+n2*t(2); % zur Kontriolle, es muss N==M sein
M =
5.1364
-0.8636
Grafik
plot(M(1),M(2),'r*') phi = linspace(0,2*pi,361); % Radius berechnen rad = norm(M-A); [x,y] = pol2cart(phi,rad); x = x+M(1); y = y+M(2); plot(x,y,'-r'); axis equal
Inkreis
Normalen berechnen, Normalen zeigen nach außen falls Richtungssinn von ABC math. positiv ist.
n1 = cross( [B-A; 0], [0;0;1]); n1(3) = []; n1 = n1/norm(n1); n2 = cross( [C-B; 0], [0;0;1]); n2(3) = []; n2 = n2/norm(n2); n3 = cross( [A-C; 0], [0;0;1]); n3(3) = []; n3 = n3/norm(n3);
Gleichungssystem loesen
Mat = [ n1', 1; n2', 1; n3', 1];
f = [ dot(A,n1); dot(B,n2); dot(C,n3)];
x = Mat\f;
% Mittelpkt und Radius aus Loesung holen
M = x(1:2);
rad = x(3);
Grafik
plot(M(1),M(2),'b*') phi = linspace(0,2*pi,361); [x,y] = pol2cart(phi,rad); x = x+M(1); y = y+M(2); plot(x,y,'-b'); legend('geg. Dreieck','Mittelpunkt',' Umkreis','Mittelpunkt',' Inkreis');