CompMath-Vorlesung 22.10.2021
Matrizen: Operationen, Loesen von Gleichungssystemen, spezielle Funktionen
Contents
Elementweise Operationen +, -, .*, ./, .\, .^
close all; clc; clear; disp('elementweise Operationen') x = 1:2:9; % 1 x 5 Matrix (Zeilenvektor) z = x+2; % 1 x 5 Matrix (Zeilenvektor) y = x.'; % 5 x 1 Matrix (Spaltenvektor) v = x + z; % 1 x 5 Matrix w = x.*z; % 1 x 5 Matrix % s = x-y % Fehler, da Dimensionen ungleich s = x.'-y; % 5 x 1 Matrix whos
elementweise Operationen Name Size Bytes Class Attributes s 5x1 40 double v 1x5 40 double w 1x5 40 double x 1x5 40 double y 5x1 40 double z 1x5 40 double
Analog elementweise mit Matrizen
A = [ 2 0 -1; -1 1 4 ]; % 2x3 Matrix B = [ 3 1 0; 1 0 -2 ]; % 2x3 Matrix C = A+B; % 2x3 Matrix D = A.*B; % 2x3 Matrix whos A B C D
Name Size Bytes Class Attributes A 2x3 48 double B 2x3 48 double C 2x3 48 double D 2x3 48 double
Matrixoperationen (+,-), *, /, \, ^
Kompatibilitaetsbedingung
disp('Matrixoperationen') %E = A*B; % Fehler, Dimensionen inkompatibel % Transponieren von B B = B.'; whos A B E = A*B % (Matrix 2x3) * (Matrix 3x2) ==> 2x2 Matrix whos E % Sonderfall potenzieren: % A^2 ==> Fehler, da A keine quadratische Matrix ist (#Zeilen == #Spalten) E^2 % E ist quadratische Matrix ==> E*E moeglich % desgleichen mit Vektoren v1 = x .* y.'; % Elementweise 1x5 v2 = x.' .* y ; % Elementweise 5x1 v3 = x*y; % Matrixweise (1x5)*(5x1) ==> 1x1 Matrix v4 = y*x; % Matrixweise (5x1)*(1x5) ==> 5x5 Matrix
Matrixoperationen
Name Size Bytes Class Attributes
A 2x3 48 double
B 3x2 48 double
E =
6 4
-2 -9
Name Size Bytes Class Attributes
E 2x2 32 double
ans =
28 -12
6 73
Loese lineares Gleichungssystem
3x - 2y -z = 0
y +z = 2
-x +3y = 2disp('Loesen eines (quadratischen, linearen) Gleichungssytems') A = [3 -2 -1; 0 1 1; -1 3 0]; f = [0; 2; 2]; x = A\f; % Loest A * x = f linksseitig disp(x) % Probe; fp = A*x; % Residuum res = f-A*x; nr = norm(res); disp(['Norm des Residuums: ',num2str(nr)] )
Loesen eines (quadratischen, linearen) Gleichungssytems
1
1
1
Norm des Residuums: 0
Was passiert bei x/(1+x)? "/"-Operator
x = 1:10; % re-definition of x xq = x/(1+x) % rechtsseitiges Loesen eines GlS whos x xq % skalar statt gewuenschter Vektor
xq =
0.8713
Name Size Bytes Class Attributes
x 1x10 80 double
xq 1x1 8 double
spezielle Funktionen
disp('Spezielle Funktionen fuer Matrizen') size(A) % Anzahl der Elemente pro Dimension numel(A) % Gesamtanzahl der Elemente % letzte Zeile A(end,:) % zeros, ones, rand, eye, diag ones(5) C = diag(1:5); p = diag(C)
Spezielle Funktionen fuer Matrizen
ans =
3 3
ans =
9
ans =
-1 3 0
ans =
1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1
p =
1
2
3
4
5
Hoeherdimensionale Matrizen
siehe view_jpg.m
Meshgrid und Visualisierung einer Funktion z(x,y)
(x,y) aus [1, 2]x[0.5, 2.5]
x = linspace(1,2,31); % x aus [1,2] y = linspace(0.5,2.5,15); % y aus [0.5,2.5] [xx,yy] = meshgrid(x,y); % Gitternetz erzeugen zz = sin(3*pi*xx).*exp(2-yy); % zz(xx,yy) Gitterkoordinaten verwenden !! surf(xx,yy,zz) % Visualisiere die durch (xx,yy,zz) beschriebene Flaeche
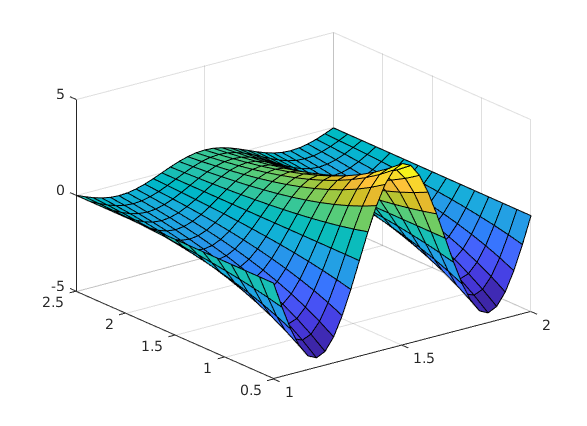
publish('v_3_a.m')