Contents
- CompMath-Vorlesung 4.11.2022
- Kurve in 2D via Funktion
- Kurve in 2D via Wertetabelle
- parametrisierte Kurve in 2D via Funktion
- parametrisierte Kurve in 2D via Wertetabelle
- Parametrisierte Kurve in 3D via Funktion
- Parametrisierte Kurve in 3D via Wertetabelle
- Beispiel kartesisches Blatt
- Flaeche im Raum (fsurf, kartesische Koord.)
- Flaeche im Raum (surf, kartesische Koord.)
- dieselbe Flaeche im Raum (surf, Polarkoordinaten)
- Kugel (sphere + surf)
- und Kugel als Ellipsoid (x-Koord. des Mittelpunktes nochmals verschoben)
- Kreis via cylinder
- Oberflache eines Oktaeders via Einzelflaechen und fill3
- Oberflache eines Oktaeders via trisurf
- Wuerfel in 5 Tetraeder zerlegt
- Wuerfel via patch
- Wuerfel via 'box on'
- You have publish manually from the command window in case of figures
CompMath-Vorlesung 4.11.2022
Kurven; Flaechen, Koerper im Raum
close all; clear; clc
Kurve in 2D via Funktion
Graph von sin(x) mit x aus [-5,5]
fplot(@(x) sin(x),[-5,5])
title('sin(x) via Funktion')
Kurve in 2D via Wertetabelle
x = linspace(-5,5,101); y = sin(x); plot(x,y) title('sin(x) via Wertetabelle') % see also: comet, semilogx, semilogy, loglog, plotyy, fill
parametrisierte Kurve in 2D via Funktion
Beispiel Kreis via Funktion
fplot(@(phi) cos(phi), @(phi) sin(phi), [0,2*pi]) axis equal title('Kreis via Funktion')
parametrisierte Kurve in 2D via Wertetabelle
phi = linspace(0,2*pi,61); % Parameter x = cos(phi); % x(phi) y = sin(phi); % y(phi) plot(x,y) axis equal title('Kreis via Wertetabelle') % see also: polarplot, pol2cart, cart2pol
Parametrisierte Kurve in 3D via Funktion
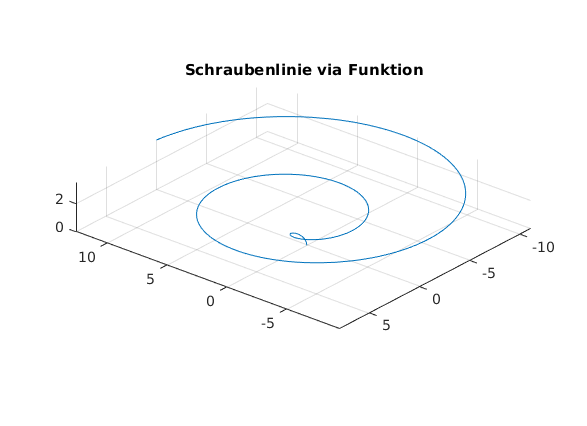
eine Schraubenlinie via Funktion
fplot3(@(t) t.*cos(t), @(t) t.*sin(t), @(t) sqrt(t), [0,4*pi]) view([-140,26]) axis equal title('Schraubenlinie via Funktion')
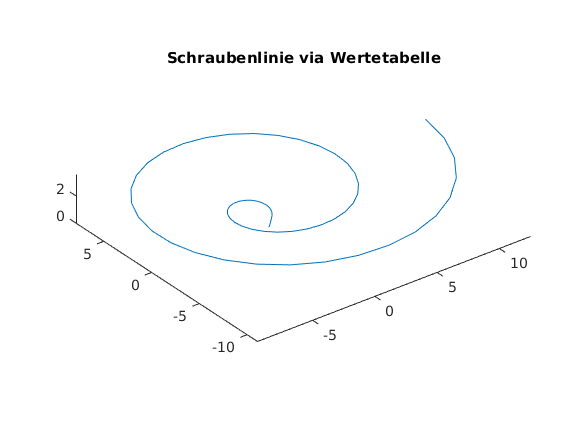
Parametrisierte Kurve in 3D via Wertetabelle
t = linspace(0,4*pi,61); % Parameter x = t.*cos(t); % x(t) y = t.*sin(t); % y(t) z = sqrt(t); % z(t) plot3(x,y,z) axis equal title('Schraubenlinie via Wertetabelle')
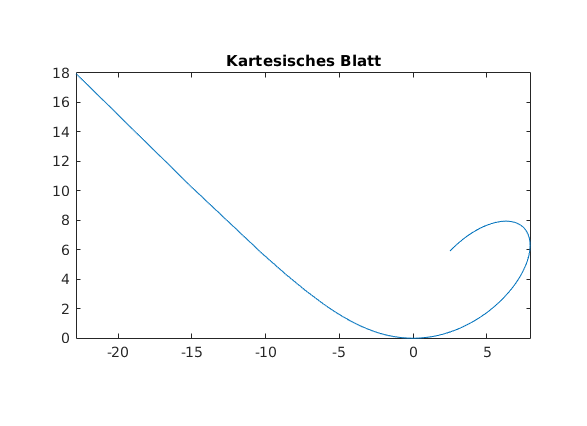
Beispiel kartesisches Blatt
a = 5; fplot(@(t) 3*a*t./(1+t.^3), @(t) 3*a*t.^2./(1+t.^3), [-pi/4,3*pi/4]) axis equal title('Kartesisches Blatt') % see also: comet3, fill3
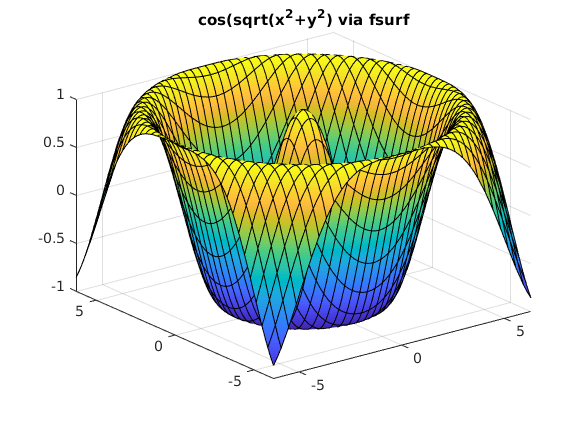
Flaeche im Raum (fsurf, kartesische Koord.)
% z(x,y) = cos(sqrt(x^2+y^2)) clear, clc, clf fsurf(@(x,y) cos(sqrt(x.^2+y.^2)), [-2*pi,2*pi]) title('cos(sqrt(x^2+y^2) via fsurf')
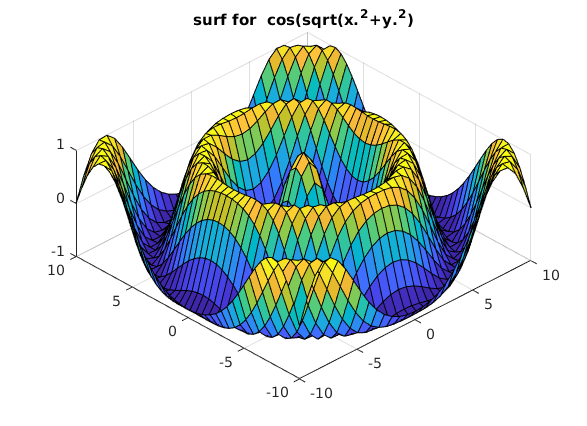
Flaeche im Raum (surf, kartesische Koord.)
clear, clc, clf % x = linspace(-10,10,31); y = linspace(-10,10,41); % [XX,YY] = meshgrid(x,y); % logisches Rechteckgitter (Tensorprodukt) ZZ = cos(sqrt(XX.^2+YY.^2)); surf(XX,YY,ZZ) title('surf for cos(sqrt(x.^2+y.^2)') view([-44,58]); % snapnow
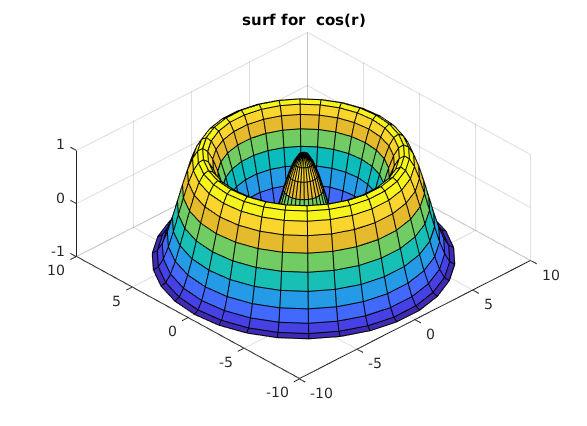
dieselbe Flaeche im Raum (surf, Polarkoordinaten)
Zeichnen von z(x,y) = z(phi,r)
clear, clc, clf % phi = linspace(0,2*pi,31); % 1D Koord. erzeugen r = linspace(0,3*pi,31); [PP,RR] = meshgrid(phi,r); % Gitter erzeugen ZZ = cos(RR); % z(phi,r) wie oben %ZZ = cos(RR)./(RR+1); % interessantere Fkt. [XX,YY,ZZ] = pol2cart(PP,RR,ZZ); % Konvertiere in kartesische Koord. surf(XX,YY,ZZ); title('surf for cos(r)') view([-44,58]);
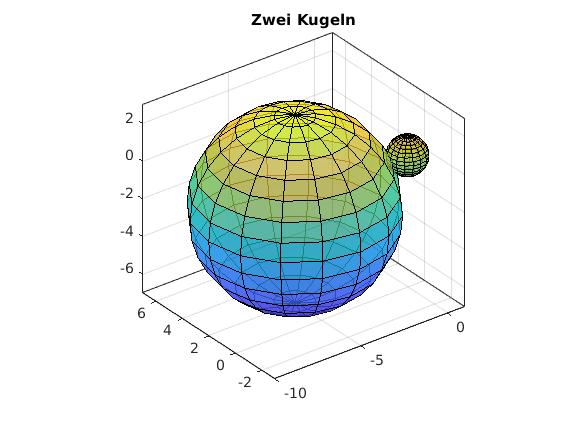
Kugel (sphere + surf)
clear, clc, clf % Kugel in Mittelpunktslage mit Radius 1 [XX,YY,ZZ] = sphere(16); % Gitter der Kugeloberflaeche surf(XX,YY,ZZ) hold on % Kugel mit Radius R und Mittelpunkt MP R = 5; MP = [-5,2,-2]; XX = XX*R + MP(1); YY = YY*R+MP(2); ZZ = ZZ.*R+MP(3); surf(XX,YY,ZZ) box on axis equal alpha(0.7); % Transparenz title('Zwei Kugeln')
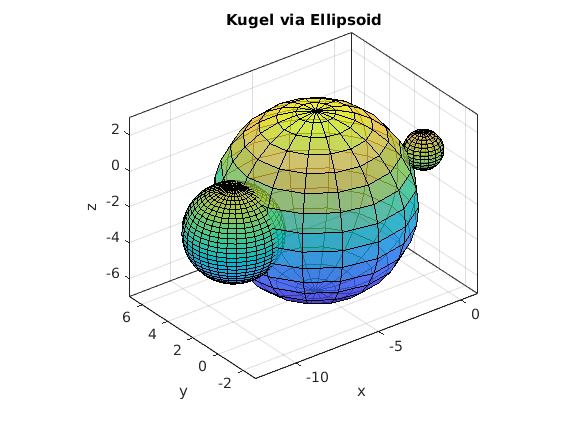
und Kugel als Ellipsoid (x-Koord. des Mittelpunktes nochmals verschoben)
[XX,YY,ZZ] = ellipsoid(MP(1)-5,MP(2),MP(3),R/2,R/2,R/2,32); surf(XX,YY,ZZ); box on axis equal xlabel('x'),ylabel('y'), zlabel('z') title('Kugel via Ellipsoid') % %% von Kugel ausgehend ein Flaeche radius(phi,theta) zeichnen % clear, clc, clf % [XX,YY,ZZ] = sphere(37); % [PP,TT,RR] = cart2sph(XX,YY,ZZ) % kartesisch --> polar % RR = RR.*(1.5+cos(2*PP)); % Radiusfunktion % [XX,YY,ZZ] = sph2cart(PP,TT,RR); % polar --> kartesisch % surf(XX,YY,ZZ); % title('von Kugel ausgehend ein Flaeche radius(phi,theta) zeichnen') % axis equal % %% Kugel: Radius mit Zufallsdaten % clear, clc, clf % [XX,YY,ZZ] = sphere(37); % [PP,TT,RR] = cart2sph(XX,YY,ZZ) % kartesisch --> polar % RR = RR.*(1+rand(size(RR))*0.15); % Radius mit Zufallsdaten % [XX,YY,ZZ] = sph2cart(PP,TT,RR); % polar --> kartesisch % surf(XX,YY,ZZ); % title('Kugel: Radius mit Zufallsdaten') % axis equal
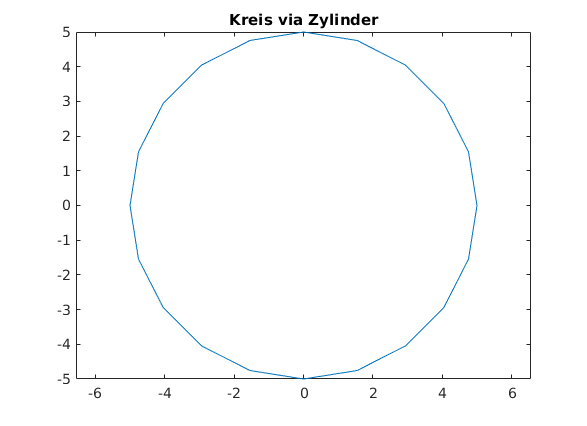
Kreis via cylinder
clear, clc, clf n = 31; % Anzahl der Punkte zur Darstellung Radius = 5; [XX,YY,ZZ] = cylinder(Radius); x = XX(1,:); y = YY(1,:); % Kreis mit Mittelpunk (0,0) clear XX YY ZZ % nicht mehr benoetigte Matrizen plot(x,y) axis equal title('Kreis via Zylinder')
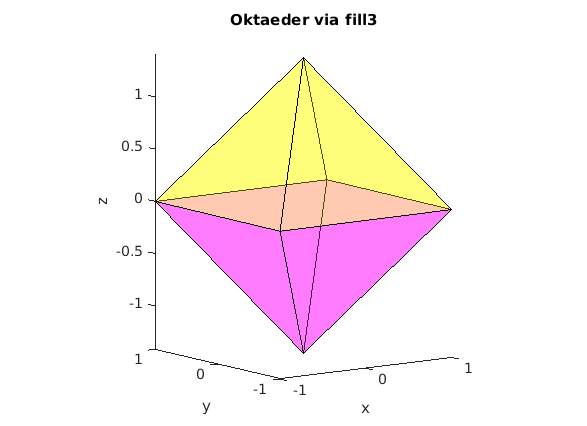
Oberflache eines Oktaeders via Einzelflaechen und fill3
clear, clc, clf % Eckpunkte zeilenweise P = [ 1 1 0 ; ... -1 1 0 ; ... -1 -1 0 ; ... 1 -1 0 ; ... 0 0 sqrt(2); ... 0 0 -sqrt(2) ] % idx = [1 2 5] ; % Indexvektor: Welche Punkte? fill3( P(idx,1), P(idx,2), P(idx,3), 'y' ); hold on idx = [2 3 5] ; % Indexvektor: Welche Punkte? fill3( P(idx,1), P(idx,2), P(idx,3), 'y' ); % idx = [3 4 5] ; fill3( P(idx,1), P(idx,2), P(idx,3), 'y' ); % idx = [4 1 5]; fill3( P(idx,1), P(idx,2), P(idx,3), 'y' ); % idx = [1 2 6] ; % Indexvektor: Welche Punkte? fill3( P(idx,1), P(idx,2), P(idx,3), 'm' ); % idx = [2 3 6]; % Indexvektor: Welche Punkte? fill3( P(idx,1), P(idx,2), P(idx,3), 'm' ); % idx = [3 4 6]; fill3( P(idx,1), P(idx,2), P(idx,3), 'm' ); % idx = [4 1 6]; fill3( P(idx,1), P(idx,2), P(idx,3), 'm' ); alpha(0.3); % Mass der Undurchsichtigkeit aus [0,1] axis equal idx = [1 2 3 4]; % Mittelebene %fill3( P(idx,1), P(idx,2), P(idx,3), 'r' ); xlabel('x'); ylabel('y'); zlabel('z') title('Oktaeder via fill3') view([-36,10])
P =
1.0000 1.0000 0
-1.0000 1.0000 0
-1.0000 -1.0000 0
1.0000 -1.0000 0
0 0 1.4142
0 0 -1.4142
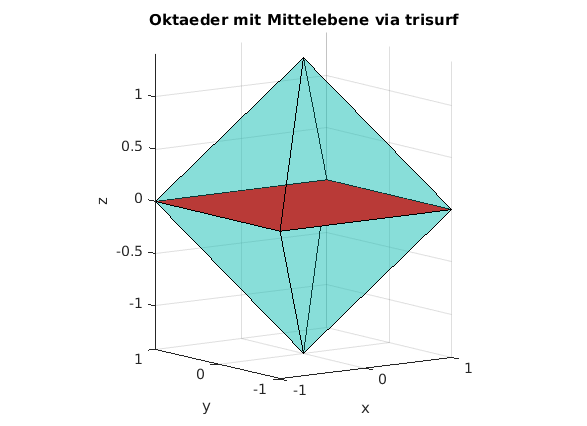
Oberflache eines Oktaeders via trisurf
clear, clc, clf % Eckpunkte zeilenweise verts = [ 1 1 0 ; ... -1 1 0 ; ... -1 -1 0 ; ... 1 -1 0 ; ... 0 0 sqrt(2); ... 0 0 -sqrt(2) ] % Beschreibung der Teildreiecke (connectivity matrix) % faces = [ 1 2 5 ; ... 2 3 5 ; ... 3 4 5 ; ... 4 1 5 ; ... 1 2 6 ; ... 2 3 6 ; ... 3 4 6 ; ... 4 1 6 ] trisurf(faces, verts(:,1), verts(:,2), verts(:,3) ) alpha(0.3); % Mass der Undurchsichtigkeit aus [0,1] axis equal % und nun noch die Mittelebene einzeichnen hold on idx = [1 2 3 4]; % Indizes der Eckpunkte fill3( verts(idx,1), verts(idx,2), verts(idx,3), 'r' ); xlabel('x'); ylabel('y'); zlabel('z') title('Oktaeder mit Mittelebene via trisurf') view([-36,10])
verts =
1.0000 1.0000 0
-1.0000 1.0000 0
-1.0000 -1.0000 0
1.0000 -1.0000 0
0 0 1.4142
0 0 -1.4142
faces =
1 2 5
2 3 5
3 4 5
4 1 5
1 2 6
2 3 6
3 4 6
4 1 6
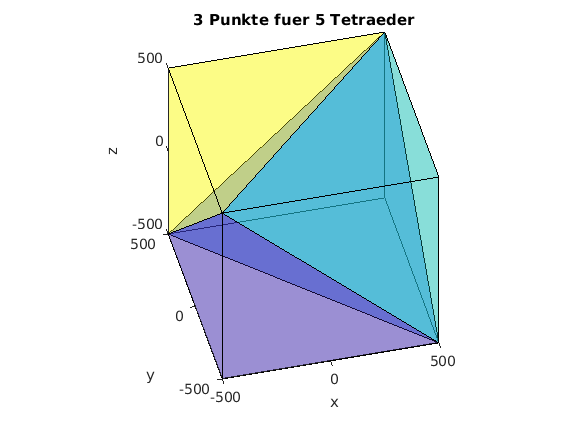
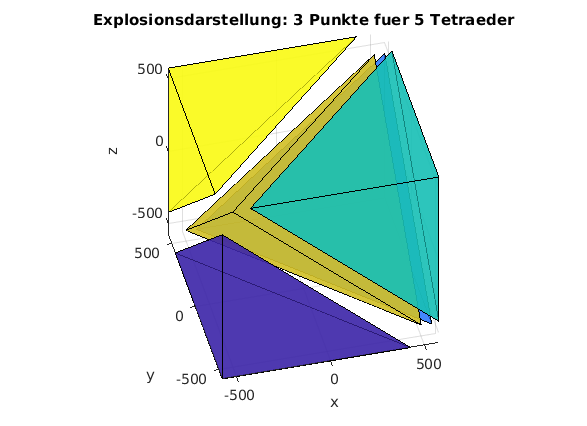
Wuerfel in 5 Tetraeder zerlegt
clear, clc, clf % Koordinaten der Eckpunkte KK = [-500 -500 -500;... 500 -500 -500;... -500 500 -500;... 500 500 -500;... -500 -500 500;... 500 -500 500;... -500 500 500;... 500 500 500]; % Zuordnung der Eckpunkte zu den Tetraedern (C-Indexing) Tets = [ 0 1 2 4; 2 1 3 7; 1 4 5 7; 1 2 4 7; 4 2 6 7]; %Tets = [ 0 1 2 4; 2 1 3 7; 1 4 5 7; 1 2 4 7]; % --> Matlab Indexing Tets = Tets+1; nelem = size(Tets,1); % Anzahl der Tetraeder nnode = size(KK,2); % Anzahl der Eckpunkte % Alle Tetraeser zeichnen figure(1) tetramesh(Tets,KK,'FaceAlpha',0.3,'Visible','on') xlabel('x'),ylabel('y'),zlabel('z') title([num2str(nnode),' Punkte fuer ',num2str(nelem),' Tetraeder']) view([-14,42]) % alpha(0.7) axis equal % Tetraeder in Explosionsdarstellung figure(2) MM = mean(KK); % Mittelpunkt aller Eckpunkte for k=1:nelem id = Tets(k,:) % Eckpunkte aktuelles Tetraeder XYZ = KK(id,:); % Koordinaten aktuelles Tetraeder mid = mean(XYZ); % Mittelpunkt aktuelles Tetraeder shift = (mid-MM)*0.3; % Explosionsverschiebung XYZ = XYZ+repmat(shift,4,1); elemk = [1 2 3; 1 2 4; 1 3 4; 2 3 4 ]; % Oberflaechen des Test in lokaler Numerierung trisurf(elemk,XYZ(:,1),XYZ(:,2),XYZ(:,3),k) hold on end xlabel('x'),ylabel('y'),zlabel('z') title(['Explosionsdarstellung: ',num2str(nnode),' Punkte fuer ',num2str(nelem),' Tetraeder']) view([-14,42]) alpha(0.7) axis equal
id =
1 2 3 5
id =
3 2 4 8
id =
2 5 6 8
id =
2 3 5 8
id =
5 3 7 8
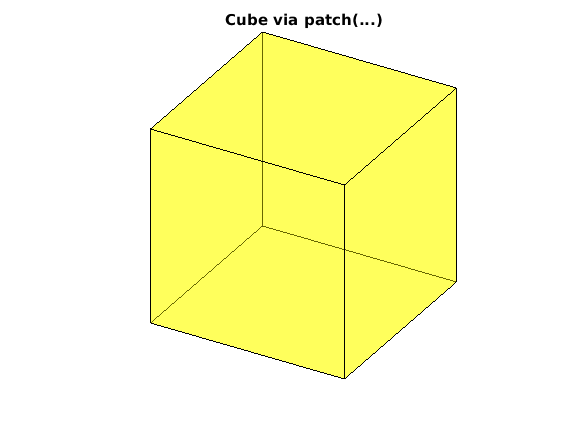
Wuerfel via patch
Create six rectangular faces, each having four vertices, by specifying the x-, y-, and z-coordinates of each vertex:
clear, clc, clf verts = [ 0 0 0; ... % the 8 vertices of th cube 1 0 0; ... 0 1 0; ... 1 1 0; ... 0 0 1; ... 1 0 1; ... 0 1 1; ... 1 1 1 ]; faces = [ 1 2 4 3; ... % the 6 faces of the cube 5 6 8 7; ... 1 2 6 5; ... 2 4 8 6; ... 4 3 7 8; ... 3 1 5 7 ]; patchinfo.Vertices = verts; patchinfo.Faces = faces; patchinfo.FaceColor = 'y'; % 'w' for white patch(patchinfo); view([30,30]) alpha(0.4) axis equal axis off title('Cube via patch(...)')
Wuerfel via 'box on'
clear, clc, clf % plot3([0,1],[0,1],[0,1],'.') % unsichtbare Diagonale des Wuerfels box on axis equal xlabel('x'),ylabel('y'),zlabel('z') title('Cube via box on')
You have publish manually from the command window in case of figures
see MATLAB answers.
publish('v_6_a.m');